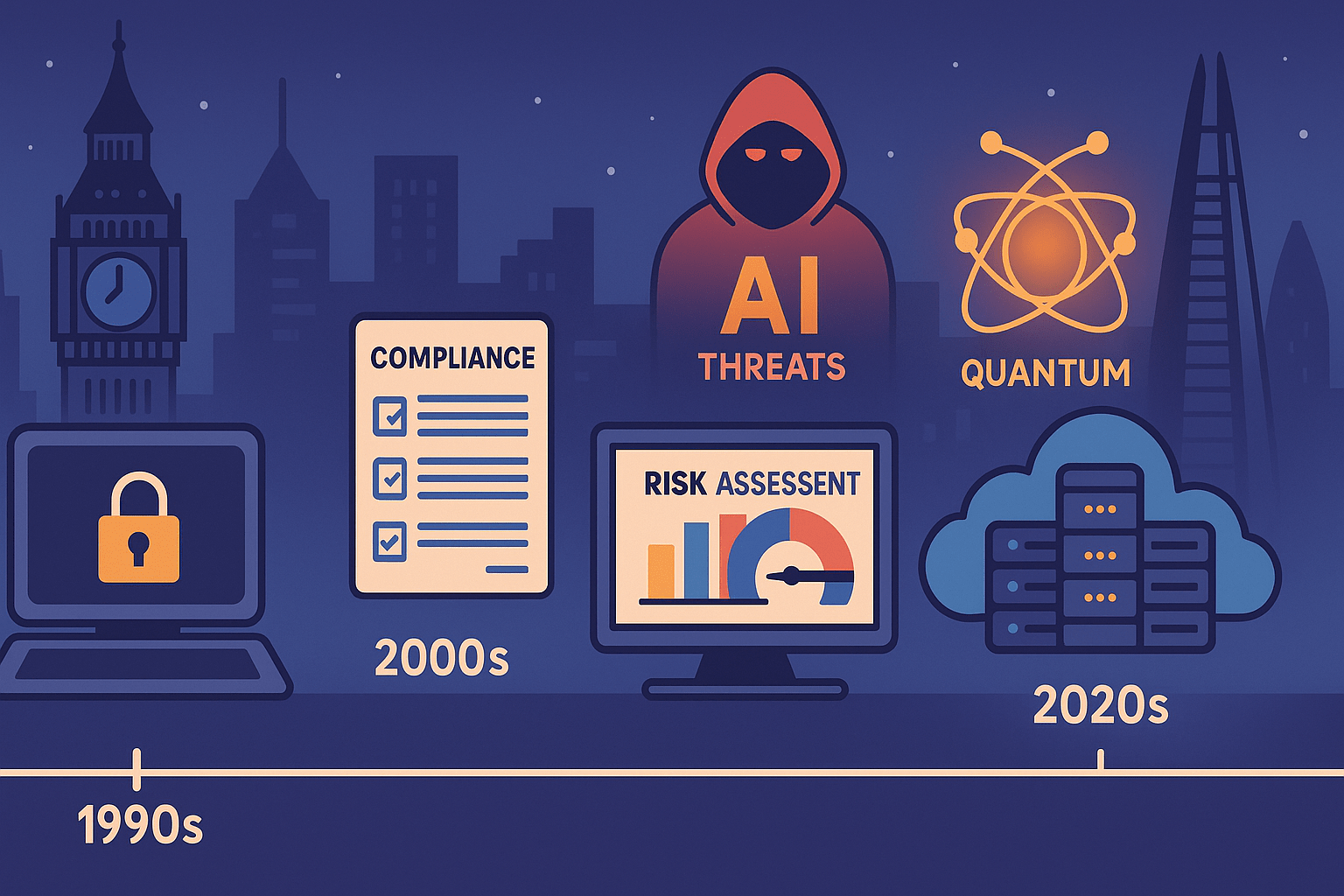
Cybersecurity feels foundational today, but as a discipline, it is startlingly young. This article argues that cyber is still in its infancy, especially when compared to IT or financial governance, and outlines why this newness matters. From AI security and quantum disruption to the structural challenges facing certification, education, and regulation, the piece maps both future directions and the underlying trends shaping the field. In a world where cyber is everywhere, this article insists: we’re just getting started.
Continue reading